01 Introduction to Chemistry
02 The Structure of Atoms
2.1 The Basic Concept of Matter
2 Lessons
03 Concept of Mole, Formulae and Equations
3.2 Concept of Mole
3 Lessons
3.3 Chemical Formulae
2 Lessons
04 Periodic Table of Elements
4.5 Group 17 Elements
2 Lessons
5.3 Covalent Bonds
1 Lesson
4.6.1 Elements in Period 3
The Period
- The period is the horizontal rows of elements in the Periodic Table.
- The modern periodic table has 7 periods.
- The period number indicates the number of electron shell.
- Elements in the same period have same number of electron shells.
- The proton number of elements increases from left to right crossing the period.
- The number of electrons also increases from left to right crossing the period.
Lanthanide and Actinide Series
- The sixth period has 32 elements. Due to short of space, 14 elements in the transition metal group are removed from the same horizontal row and is placed below the main table, These elements are called the Lanthanide Series.
- The seven-period also has 32 elements. With the same reason, 14 elements are removed from the same horizontal row and are placed below the main table, These elements are called the Actinide Series.
Physical Change Across a Period
There are a few major changes in physical properties across a period. For example,
- the state of matter changes across the period.
- The size of the molecule changes across the period, too.
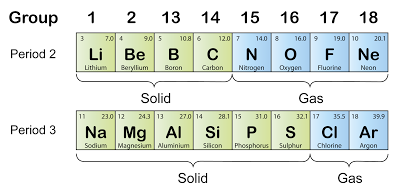
State of Matter
- The diagram above shows that the state of matter of the elements in period 2 and period 3 change from solid to gas across the period (At room temperature).
- In period 2, the first 4 elements are solid whereas the last 4 elements are gases. The melting point of lithium is low while the melting point of boron and carbon is very high.
- In period 3, the first 6 elements are solid whereas the last 2 elements are gases.
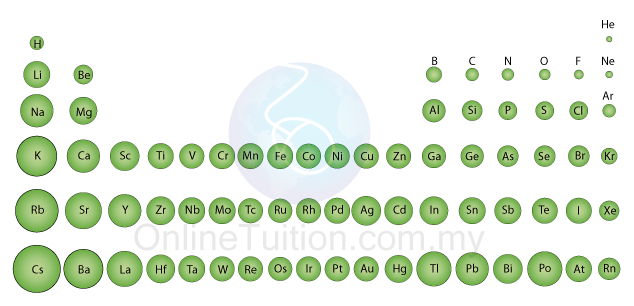
Atomic Size
- As shown in the diagram above, the atomic size of elements in period 2 and period 3 decreases across a period.
- This is because
- The number of proton in the nucleus increases whereas the number of shells remains unchanged across a period.
- As the number of proton in the nucleus increases, the positive charge of the nucleus will also increase.
- The negative charge of the valence electrons will also increase due to the increase in the number of valence electrons across a period.
- Thus, the attraction force between the nucleus and the valence electrons is getting stronger and stronger across a period.
- This force will pull the valence electrons closer to the nucleus and thus reduces the atomic radius.
- Therefore the size of the atom decreases across a period from left to right.
- The diagram below shows the change in the atomic size of the elements in all seven periods. The trends can be concluded as below:
- The size of the atom increases down the group.
- The size of the atom decreases across a period from left to right.
- For transition metal, the size of the atom does not have obvious change across a period.
Chemical Properties Change Across a Period
- There is a gradual chemical change across a period.
- The acidity (or basicity) of the oxide of element changes across a period.
- The metallic properties, the electronegativity of the element also change across a period.
Acidic Oxide or Basic Oxide
From left to right across a period the oxides change from alkaline/basic (with metals e.g. Na2O) to acidic (with non-metals e.g. SO2).
Metal, Metalloid and Non-metal
- As we go across a period from left to right, the elements change from metals to non-metals.
- There are about 7 elements in the periodic table are classified as semi-metals.
- The metals in the periodic table are mainly found in the left-hand columns (Groups 1 and 2) and in the central blocks of the transition elements.
- On the right-hand side of the periodic table, there are 7 semi-metals form a staircase-like pattern, act as a divider between metal and non-metal.
- The semi-metals are also called the metalloid.
Uses of Metalloids
- The most widely used semi-metals are silicon and germanium.
- It is used to make diodes and transistors in the electronics industry.
Electronegativity
- Electronegativity is a measure of the potential of atoms to attract electrons to form negative ions.
- Metals have low electronegativities.
- Non-metals have high electronegativities.
- Electronegativities of the elements increase across a period with increasing proton number. This is because
- as the proton number increases, the positive charge of the nucleus will increase accordingly.
- this will increase the ability of the atom to attract electrons from the surrounding and thus increase the electronegativity of the atom.